High Speed EServer
The High Speed EServer is a communication protocol that allows you to connect to a Yaskawa robot controller.
- Features
- Connect to the Robot
- Move robot
- Get cartesian position
- Get joint position, error and torque
- Alarms
- Get Alarms
- Robot Status
- Servo commands
- Switching commands
- Display popup message on Pendant
- Job
- Read and Write IO Signals
- Read and Write Registers
- Read and Write Byte Data
- Read and Write Integer Data
- Read and Write Double Precision Data
- Read and Write Single Precision Data
- Read and Write 16-Byte Character Data
- Read and Write Position Variables
- Read and Write Base Position
- File handling
- Configure your robot
Features
Connect to the Robot
// Connect to the robotvar robot = new YaskawaRobot();robot.Connect("192.168.0.1");// Ensure robot is connectedbool isConnected = robot.HighSpeedEServer.Connected;
Move robot
To move the robot, your robot must be correctly configured, see the section below.
Move Cartesian
robot.HighSpeedEServer.MoveCartesian(x: 1000,y: 10,z: 0,rx: 0,ry: 0,rz: 0,PositionCommandClassification.Cartesian_MM_S,speed:10,PositionCommandOperationCoordinate.Robot);
| Argument name | Argument type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| x | Double | X coordinate in millimeter | |
| y | Double | Y coordinate in millimeter | |
| z | Double | Z coordinate in millimeter | |
| rx | Double | Rx coordinate in degrees | |
| ry | Double | Ry coordinate in degrees | |
| rz | Double | Rz coordinate in degrees | |
| classification | PositionCommandClassification | Unit for speed (LinkPercent, Cartesian_MM_S, Cartesian_DEG_S) | |
| speed | Double | Move speed | |
| coordinate | PositionCommandOperationCoordinate | Frame coordinate (Base, Robot, User, Tool) | |
| posture | RobotPosture | ✅ | Robot target posture (RCONF) |
| commandtype | PositionCommandType | ✅ | Command type (LinkAbsolute, StraightAbsolute, StraightIncrement) |
| RobotControlGroup | Integer | ✅ | Control group (default: 1) |
| StationControlGroup | Integer | ✅ | Station control group (default: 0) |
| tool | Integer | ✅ | Selected TCP (default: 0) |
| userCoordinate | Integer | ✅ | User coordinate for User coordinate (default: 0) |
Move joint
robot.HighSpeedEServer.MoveJoints(new int[] { 1000, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, PositionCommandClassification.LinkPercent, 10);
| Argument name | Argument type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| axesPulse | Integer[] | Axes position in degrees | |
| classification | PositionCommandClassification | Classification (LinkPercent, Cartesian_MM_S, Cartesian_DEG_S) | |
| speed | Double | Movement speed in degrees/s | |
| commandtype | PositionCommandType | ✅ | Command type (LinkAbsolute, StraightAbsolute, StraightIncrement) (default: StraightIncrement) |
| RobotControlGroup | Integer | ✅ | Robot control group (default: 1) |
| StationControlGroup | Integer | ✅ | Station control group (default: 1) |
| tool | Integer | ✅ | Selected TCP (default: 0) |
Robot position
Get cartesian position
RobotPositionCartesianData position = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetRobotCartesianPosition();
Properties of class RobotPositionCartesianData :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Form | RobotPosture |
| DataType | RobotPositionDataType |
| ToolNumber | Integer |
| UserCoordinateNumber | Integer |
| X | Double |
| Y | Double |
| Z | Double |
| Rx | Double |
| Ry | Double |
| Rz | Double |
Get joint position, error and torque
// Get position pulses of each axesRobotPositionData(Of Integer) position = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetRobotJointPosition();// Get position error of each axes in pulsesRobotPositionData(Of Integer) error = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetPositionError();// Get torque in mNm of each axesRobotPositionData(Of Integer) torque = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetTorque();
Properties of class RobotPositionData(Of Integer) :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Form | RobotPosture |
| DataType | RobotPositionDataType |
| ToolNumber | Integer |
| UserCoordinateNumber | Integer |
| Axes | Integer[] |
Alarms
Reset Alarms
robot.HighSpeedEServer.AlarmReset(AlarmResetType.Reset);
Get Alarms
RobotAlarmData alarm = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetAlarm(RobotRecentAlarm.Latest);
Members of enum RobotRecentAlarm :
| RobotRecentAlarm | Value |
|---|---|
| Latest | 1 |
| SecondLatest | 2 |
| ThirdLatest | 3 |
| FourthLatest | 4 |
Properties of class RobotAlarmData :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Code | Integer |
| Data | Integer |
| Type | Integer |
| OccurringTime | String |
| Text | String |
Robot Status
RobotStatusData statusData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetStatusInformation();
Properties of class RobotStatusData :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Step | Boolean |
| Cycle | Boolean |
| Automatic | Boolean |
| Running | Boolean |
| InGuardSafeOperation | Boolean |
| Teach | Boolean |
| Play | Boolean |
| CommandRemote | Boolean |
| InHoldStatusPendant | Boolean |
| InHoldStatusExternally | Boolean |
| InHoldStatusByCommand | Boolean |
| Alarming | Boolean |
| ErrorOccurring | Boolean |
| ServoOn | Boolean |
Servo commands
To send servo commands, your robot must be correctly configured, see the section below.
/// Servo onrobot.HighSpeedEServer.ServoCommand(OnOffCommandType.Servo, true);/// Servo offrobot.HighSpeedEServer.ServoCommand(OnOffCommandType.Servo, false);
Members of enum OnOffCommandType :
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Hold | 1 |
| Servo | 2 |
| HLock | 3 |
Switching commands
robot.HighSpeedEServer.SwitchingCommand(SwitchingCommands.Cycle);
Members of enum SwitchingCommands :
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Cycle | 1 |
| Step | 2 |
| Continue | 3 |
Display popup message on Pendant
robot.HighSpeedEServer.Display("Hello !");
Job
Select and start job
To select and start a job, your robot must be correctly configured, see the section below.
robot.HighSpeedEServer.SelectJob("PROGRAM", line:0);robot.HighSpeedEServer.StartJob();```#### Get executing job information```csharpRobotJobData jobInformation = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetExecutingJobInformation();
Properties of class RobotJobData :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Name | String |
| Line | Integer |
| Step | Integer |
| SpeedOverride | Integer |
Read and Write IO Signals
Description:
The ReadIO and WriteIO functions allow reading and writing robot I/O signals. These include user input signals, user output signals, external signals, network signals, and system control signals.
First index :
- 1 to 512 : Robot user input signal
- 1001 to 1512: Robot user output signal
- 2001 to 2512: External input signal
- 2701 to 2956: Network input signal
- 3001 to 3512: External output signal
- 3701 to 3956: Network output signal
- 4001 to 4160: Robot system input signal
- 5001 to 5300: Robot system output signal
- 6001 to 6064: Interface panel input signal
- 7001 to 7999: Auxiliary relay signal
- 8001 to 8128: Robot control status signal
Example: Reading IO Data
int firstIndex = 1001; // Robot user output signalint count = 4; // Number of bytes to readvar ioData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadIO(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("IO Data: " + BitConverter.ToString(ioData.Values));
Example: Writing IO Data
int firstIndex = 1001; // Robot user output signalbyte[] dataToWrite = new byte[] { 0x01, 0x00, 0xFF, 0x00 };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteIO(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("IO Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Registers
Description:
Registers store numerical data. The ReadRegister and WriteRegister methods allow interaction with these values.
Example: Reading Register Data
int firstIndex = 10; // Starting register indexint count = 2; // Number of registers to readvar registerData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadRegister(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Register Data: " + string.Join(", ", registerData.Values));
Example: Writing Register Data
int firstIndex = 10; // Starting register indexushort[] dataToWrite = new ushort[] { 1234, 5678 };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteRegister(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("Register Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Byte Data
Description:
Reads and writes byte-type variables from the robot system.
Example: Reading Byte Data
int firstIndex = 2001; // External input signalint count = 6; // Number of bytes to readvar byteData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadByte(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Byte Data: " + BitConverter.ToString(byteData.Values));
Example: Writing Byte Data
int firstIndex = 2001; // External input signalbyte[] dataToWrite = new byte[] { 0xAA, 0xBB, 0xCC, 0xDD };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteByte(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("Byte Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Integer Data
Description:
Reads and writes integer-type variables from the robot system.
Example: Reading Integer Data
int firstIndex = 5001; // Robot system output signalint count = 4; // Number of integers to readvar intData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadInteger(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Integer Data: " + string.Join(", ", intData.Values));
Example: Writing Integer Data
int firstIndex = 5001; // Robot system output signalshort[] dataToWrite = new short[] { 100, -50, 200, -100 };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteInteger(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("Integer Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Double Precision Data
Description:
Reads and writes 64-bit floating-point values.
Example: Reading Double Data
int firstIndex = 6001; // Interface panel input signalint count = 2; // Number of doubles to readvar doubleData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadDouble(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Double Data: " + string.Join(", ", doubleData.Values));
Example: Writing Double Data
int firstIndex = 6001; // Interface panel input signaldouble[] dataToWrite = new double[] { 123.456, -78.90 };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteDouble(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("Double Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Single Precision Data
Description:
Reads and writes 32-bit floating-point values.
Example: Reading Single Data
int firstIndex = 7001; // Auxiliary relay signalint count = 3; // Number of floats to readvar floatData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadSingle(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Float Data: " + string.Join(", ", floatData.Values));
Example: Writing Single Data
int firstIndex = 7001; // Auxiliary relay signalfloat[] dataToWrite = new float[] { 1.23f, -4.56f, 7.89f };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteSingle(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("Float Data written successfully.");
Read and Write 16-Byte Character Data
Description:
Reads and writes string data, where each entry consists of 16 bytes.
Example: Reading 16-Byte Character Data
int firstIndex = 8001; // Robot control status signalint count = 2; // Number of strings to readvar charData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.Read16BytesChar(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Character Data: " + string.Join(", ", charData.Values));
Example: Writing 16-Byte Character Data
int firstIndex = 8001; // Robot control status signalstring[] dataToWrite = new string[] { "HelloRobot", "MoveFaster" };robot.HighSpeedEServer.Write16BytesChar(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("Character Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Position Variables
Description:
Reads and writes robot position data.
Example: Reading Position Variable
int firstIndex = 9001; // Robot position variable indexint count = 1; // Number of position variables to readvar positionData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadPositionVariable(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Position Data: " + positionData);
Example: Writing Position Variable
int firstIndex = 9001; // Robot position variable indexvar position = new RobotPositionData<int> { DataType = 1, Axes = new int[] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 } };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WritePositionVariable(firstIndex, new[] { position });Console.WriteLine("Position Data written successfully.");
Read and Write Base Position
Description:
Reads and writes base position data for robot movement.
Example: Reading Base Position
int firstIndex = 9101; // Base position indexint count = 1; // Number of base positions to readvar basePositionData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.ReadBasePosition(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Base Position Data: " + basePositionData);
Example: Writing Base Position
int firstIndex = 9101; // Base position indexvar basePosition = new RobotBasePositionData { DataType = RobotBasePositionType.Absolute, Axes = new int[] { 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40 } };robot.HighSpeedEServer.WriteBasePosition(firstIndex, new[] { basePosition });Console.WriteLine("Base Position Data written successfully.");
Here is the updated markdown document including the Read32BytesChar and Write32BytesChar functions.
Read and Write 32-Byte Character Data
Description:
The Read32BytesChar and Write32BytesChar functions allow reading and writing string data with a fixed size of 32 bytes per entry. Any characters beyond this limit are truncated, and shorter strings are padded with null (0x00) bytes.
Example: Reading 32-Byte Character Data in C#
int firstIndex = 8501; // Example index for reading 32-byte character dataint count = 2; // Number of string entries to readvar charData = robot.HighSpeedEServer.Read32BytesChar(firstIndex, count);Console.WriteLine("Character Data: " + string.Join(", ", charData.Values));
Example: Writing 32-Byte Character Data in C#
int firstIndex = 8501; // Example index for writing 32-byte character datastring[] dataToWrite = new string[] { "HelloRobot32Bytes", "MoveWithPrecision" };robot.HighSpeedEServer.Write32BytesChar(firstIndex, dataToWrite);Console.WriteLine("32-Byte Character Data written successfully.");
File handling
Get file list
string[] files = robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetFileList("*.JBI").Files;
Upload file on robot
robot.HighSpeedEServer.LoadFile("PROGRAM.JBI", fileContent, onLoadFileProgress);private void onLoadFileProgress(LoadFileProgress progress){// Called during file loading}
Properties of class LoadFileProgress :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Completed | Boolean |
| FileName | String |
| TotalBytes | Integer |
| LoadedBytes | Integer |
Download file from robot
robot.HighSpeedEServer.GetFile("PROGRAM.JBI", onGetFileProgress);private void onGetFileProgress(GetFileProgress progress){// Called during file loading}
Properties of class GetFileProgress :
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| Completed | Boolean |
| FileName | String |
| DownloadedBytes | Integer |
Delete file on robot
robot.HighSpeedEServer.DeleteFile("PROGRAM.JBI");
Configure your robot
Enable remote control
- Set Management mode as Security mode
- Select
IN/OUT/PSEUDO INPUT SIGNAL - Move the cursor to the #82015
CMD REMOTE SEL, and pressINTER LOCK+SELECTto select
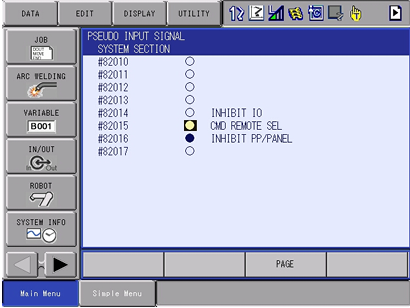
Authorize remote control with key
The read commands work regardless of the position of the physical key. However, if you want to send commands (Run job, Go to position, etc.), you need to put the key in the left position on Remote Control.

To enable this, we need to copy register #80011 (Key on Remote Position) to #40042 (Enable Remote Control) :
- Set Management mode as Security mode
- Select
IN/OUT/LADDER EDITOR - Ensure
#40042is not already written by a relay and add the following Rung :

Enable job select
To be able to authorise job select from the SDK, you need to set the permission :
- Set Management mode as Security mode
- Select
SETUP/FUNCTION ENABLE - Set
JOB SELECT WHEN REMOTE AND PLAYtoPERMIT. For advanced users or on the Smart Pendant, setSC2 224to0.
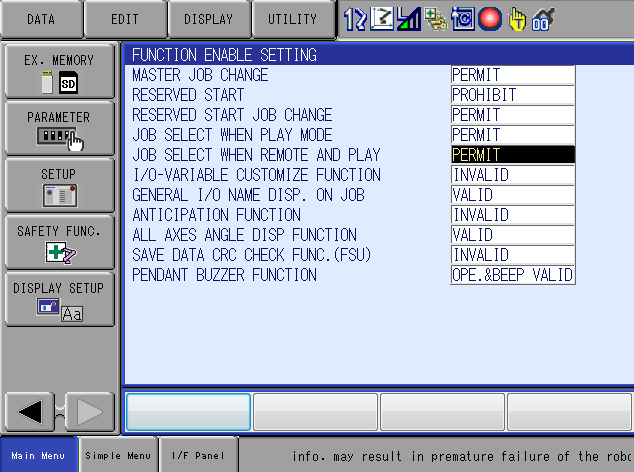
Authorise file overwriting
To enable the SDK to send files that already exist on the controller and overwrite them:
- Set Management mode as Security mode
- Select
PARAMETER/RS - Set
RS029to1 - Set
RS214to1